In September, amid a climate of startling interest rates, UK Chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng announced a series of tax cuts, including the reduction of the top personal income tax rate that applies to those earning more than £150,000 from 45% to 40%. Just ten days later, following market turmoil that saw the British Pound drop at one point to a low of $1.035 USD, its lowest level since 1985, the decision was reversed calling the cuts “a massive distraction.”
Heading into the 2022-23 Federal Budget on 25 October, the question for the Australian Government is different. It is not whether to introduce personal income tax cuts but whether to keep, amend or repeal the cuts legislated to commence on 1 July 2024.
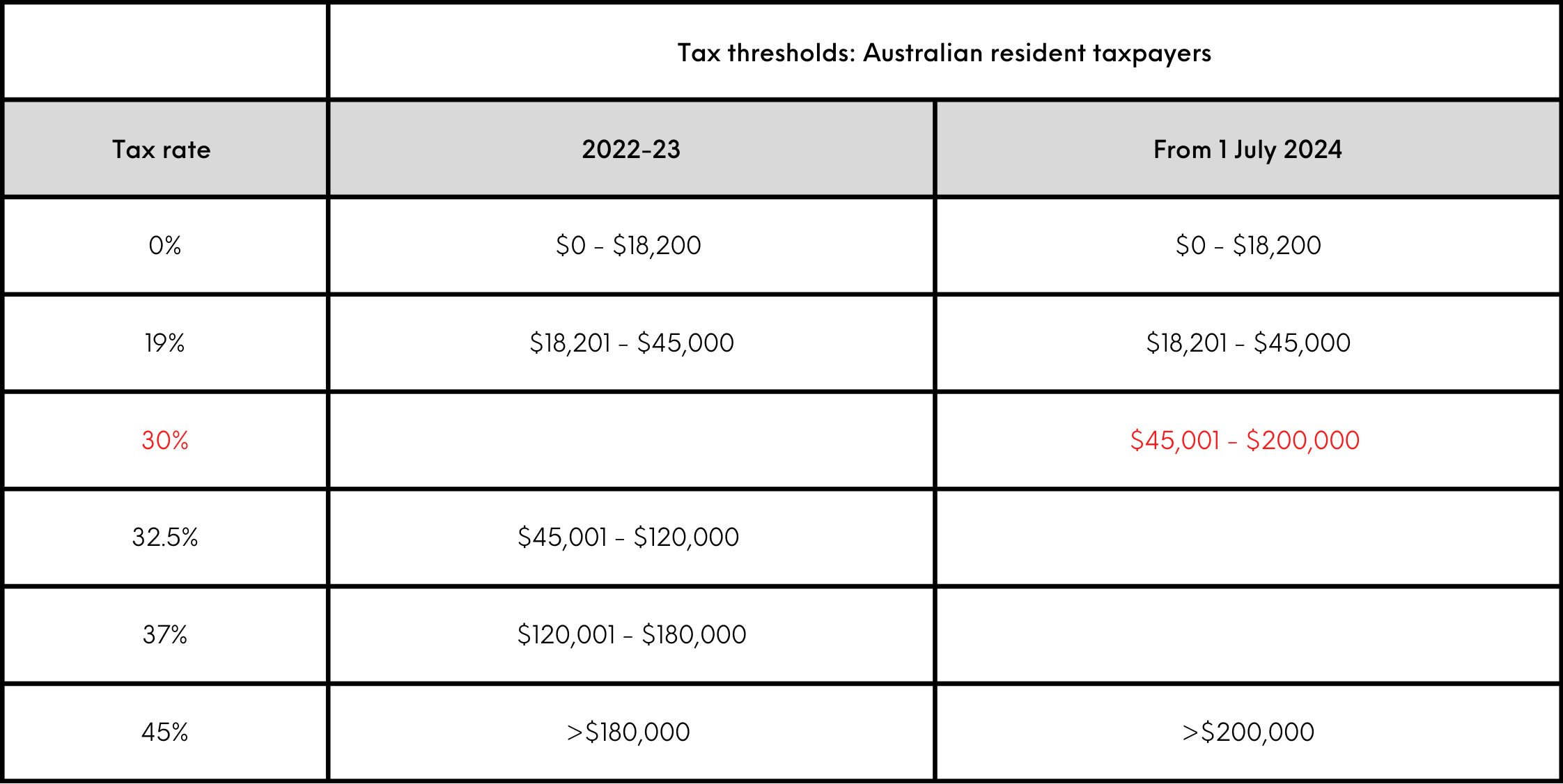
In Australia, the 2018-19 Budget introduced the Personal Income Tax Plan. The plan implemented three stages of income tax cuts over seven years that will, by 2024-25, simplify the tax brackets and enable taxpayers to earn up to $200,000 before paying a new top marginal tax rate of 45%. Stages of the plan, bringing relief for low and middle income earners, were brought forward in the 2019-20 Budget and again in 2020-21.
Labor’s pre-election Lower Taxes policy states, “An Albanese Labor Government will deliver tax relief for more than 9 million Australians through the legislated tax cuts that benefit everyone with incomes above $45,000.” But this month, the Treasurer has subtly changed the narrative from simply “our policy has not changed on stage three tax cuts” to “We do need to ensure that spending in the Budget, particularly in these uncertain global times, is geared toward what’s affordable and sustainable and responsible and sufficiently targeted. I think that’s one of the lessons from the UK.”
The public appeal of repealing the final stage three tax cuts is understandable. Back in 2018-19 when the plan was first introduced, the economy was in surplus and Australia was yet to feel the effects of a global pandemic, environmental extremities, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The tax cuts forego around $240bn of tax revenue over the next 10 years, and because it is percentage based, favours high income earners. The public policy think tank, the Grattan Institute, previously warned that if the government progressed with the stage three cuts “Australia’s income tax system will be less progressive than it’s been since the 1950s”.
Conversely, the rationale for reforming the current personal income tax regime where the highest marginal tax rate applies from around 2.5 times average full-time earnings (compared to around 4 times in Canada and 8 times in the US), is also understandable. When it comes to international competitiveness, New Zealand’s top marginal tax rate is 33% (from $180,000) and Singapore’s is 22%, increasing to 24% in 2023-24. If implemented, stage 3 of the income tax plan would see around 95% of taxpayers paying a marginal tax rate of 30% or less.
The 1 July 2024 tax cuts
Stage three of the Personal Income Tax Plan is legislated to take effect from 1 July 2024.
What the tax stats say
Personal income and withholding tax represents around 48% of the annual Commonwealth tax collections. Company tax, by comparison, is around 16%, and the goods and services tax (GST) just under 15% of total tax revenue collected.
Australia has a progressive personal tax system. That is, those with higher incomes pay not only a higher amount of tax, but a higher proportion of their income in tax. As a result, the 3.6% of taxpayers with taxable incomes of over $180,000 pay 31.6% of the total.
If you would like to discuss any of the above measures, please feel free to email your AHJ contact or enquiries@ahjackson.com or call (07) 3253 1500.

